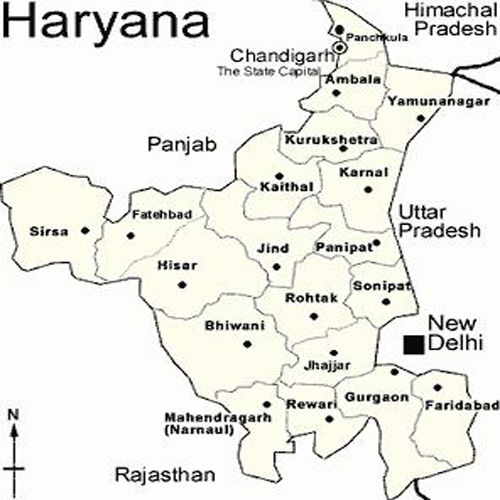
Haryana is a state in India. Historically, it has been a part of the Kuru region in North India. The name Haryana is found mentioned in the 12th century AD by the apabhramsha writer Vibudh Shridhar (VS 1189-1230). It is bordered by Punjab and Himachal Pradesh to the north, and by Rajasthan to the west and south. The river Yamuna defines its eastern border with Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh. Haryana also surrounds Delhi on three sides, forming the northern, western and southern borders of Delhi. Consequently, a large area of Haryana is included in the National Capital Region. The capital of the state is Chandigarh which is administered as a union territory and is also the capital of Punjab. The name Haryana means the Abode of God from Sanskrit Hari (the Hindu God Vishnu) and ayana (home), although it may also refer to the lush green landscape of the state (from Sanskrit harit meaning green).
TOURIST PLACES
Surajkund
Surajkund is an ancient reservoir of the 10th century, 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) away to the south west from a more ancient dam of the 8th century called the Anagpur Dam; both are located in Haryana, India. Surajkund (literal meaning is 'Lake of the Sun') is an artificial Kund (‘Kund’ means “lake” or reservoir) built in the backdrop of the Aravalli hills with an amphitheatre shaped embankment constructed in semicircular form. It is said to have been built by the Tomar king Suraj Pal of Tomar dynasty in the 10th century. Tomar was a sun worshipper and he had therefore built a Sun temple on its western bank. Another 'kund' by the same name as ‘Suraj Kund’ existed in Sunam city, a tahsil and sub division of the Sangrur District in Punjab. This was sacked by Mahmood Ghaznvi or Taimur Lane. The temple is now in ruins.
Badkhal Lake
Badkhal Lake was a natural lake situated in Faridabad, Haryana, about 16 kilometers from Delhi.It was a natural lake surrounded by hilly areas of the Aravali Range in Haryana.As of May 2009, the lake is almost a completely dried up grassy terrain and the unusually low rainfall in the area has been cited. Certain mines surrounding the lake are also responsible for blockage of flow of water to the lake's reservoir. Also some mineral water companies are responsible as well, for taking water from the lake for their purposes.On 30th November 2009, it was announced that the lake and the nearby Surajkund, would be filled up with water, by the time 2010 Commonwealth Games arrive, but no action was taken.
Manesar
Manesar is a fast growing industrial town in Gurgaon district of the State of Haryana in India, and is a part of the National Capital Region (NCR) of Delhi. It has transformed from a sleepy village to one of the fastest growing townships in India. It is an upcoming area of NCR. Some of the developers have added a new tag to Manesar calling it as `New Gurgaon'. Proximity to political nerve center - Delhi has also led the government to establish headquarters of some institutes of national importance here like the National Security Guards (and its training center), National Bomb Data Centre and National Brain Research Centre.
More than 100,000 people go to work in Manesar from adjoining places. The Gurgaon-Manesar Master Plan projects the population of 37,00,000 by 2021. It has many factories, offices, hotels and educational institutes. There are several sightseeing spots around the area, some overlapping with Gurgaon.Manesar is 32km from IGI Airport and has some of the best urban infrastructure in northern India. Located on NH 8, the area is well connected with Delhi, Jaipur, Ahmedabad and Mumbai; air connectivity is equally good.
Panipat
Panipat is an ancient and historic city in Panipat district, Haryana state, India. It is 90 km north from Delhi and 169 km south of Chandigarh on NH-1 and comes under the National Capital Region of Delhi. Three battles fought at the city were turning points in Indian history. The city is famous in India by the name of "City of Weaver".
Gurgaon
Gurgaon is the sixth largest city in the Indian state of Haryana. Gurgaon is the industrial and financial center of Haryana. It is located 30 km south of national capital New Delhi, about 10 kilometers from Dwarka Sub City and 268 km south of Chandigarh, the state capital. An important town in ancient Hindu mythology Gurgaon is one of Delhi's four major satellite cities and is part of the National Capital Region of India. According to a survey by Business Today magazine, Gurgaon is considered the best city in India to work and live in.
Gurgaon is also the only Indian city to have successfully distributed electricity connections to all its households. However, because of its heavy vehicular traffic and inefficient public transportation apart from the Delhi Metro, Gurgaon ranks 11 amongst Indian cities on the "Life after Work" index of Business Today. Gurgaon has the 3rd highest per capita income in India after Chandigarh and Mumbai.
Over the past 25 years the city has undergone rapid development and construction.A wave of multinational companies choose to locate their operations in Gurgaon after GE did so in 1997. Big companies like Airtel, American Express, EXL, IBM, Microsoft, Sapient, DLF, Maruti Suzuki, Hero Honda, Infosys, Ericsson, Oracle, Bank of America, American Airlines, The Coca-Cola Company, Nokia, etc. have made Gurgaon the call centre capital of India and an important financial center.
Haryana was the cradle of the Indus Valley and Vedic Civilizations, both flourishing on the banks of the now lost Sarasvati River. Several decisive battles were fought in the area, which shaped much of the history of India. These include the epic battle of Mahabharata at Kurukshetra (including the recital of the Bhagavad Gita by Krishna), and the three battles of Panipat. Haryana was administered as part of the Punjab province of British India, and was carved out on linguistic lines as India's 17th state in 1966. Haryana is now a leading contributor to the country's production of foodgrain and milk. Agriculture is the leading occupation for the residents of the state, the flat arable land irrigated by submersible pumps and an extensive canal system. Haryana contributed heavily to the Green Revolution that made India self-sufficient in food production in the 1960s.
Haryana is one of the wealthiest states of India and has the third highest per capita income in the country at Rs. 67,891, including the largest number of rural crorepatis in India. Haryana is also one of the most economically developed regions in South Asia and its agricultural and manufacturing industry has experienced sustained growth since 1970s. Haryana is India's largest manufacturer of passenger cars, two-wheelers, and tractors. Since 2000, the state has emerged as the largest recipient of investment per capita in India. The city of Gurgaon has rapidly emerged as a major hub for the information technology and automobile industries. Gurgaon is home to Maruti Udyog Limited, India's largest automobile manufacturer, and Hero Honda Limited, the world's largest manufacturer of two-wheelers. Yamunanagar, Panipat, Panchkula and Faridabad are also industrial hubs, with the Panipat Refinery being the second largest refinery in South Asia. There are also long established steel, plywood, paper and textile industries in the state.
Major ethnic group in Haryana is of Jat people and Yaduvanshi Ahirs. Other ethnic groups are of Kambojs, Gujjars, Agarwals, Rors, Brahmins, Rajputs, Punjabis and Sainis.Hindus are majority in Haryana and are about 90% of the population, Sikhs 6.2%, Muslims 4.05% and Christians 0.10%.
The river Yamuna flows along its eastern boundary. The ancient Sarasvati River is said to have flowed from Yamunanagar, but it has now disappeared.
The river Ghaggar is Haryana's main seasonal river. The Ghaggar rises in the outer Himalayas, between the Yamuna and the Sutlej and enters Haryana near Pinjore, Panchkula district. Passing through Ambala and Hissar, it reaches Bikaner in Rajasthan and runs a course of 290 miles before disappearing into the deserts of Rajasthan.
The Markanda river's ancient name was Aruna. A seasonal stream like the Ghaggar, it originates from the lower Sivalik Hills and enters Haryana near Ambala. During monsoons, this stream swells into a raging torrent notorious for its devastating power. The surplus water is carried on to the Sanisa lake where the Markanda joins the Sarasvati.
An important tributary is the Tangri. The Sahibi originates in the Mewat hills near Jitgarh and Manoharpur in Rajasthan. Gathering volume from about a hundred tributaries, it reaches voluminous proportions, forming a broad stream around Alwar and Patan. On reaching Rohtak it branches off into two smaller streams, finally reaching the outskirts of Delhi and flowing into the Yamuna. There are three other rivulets in and around the Mewat hills – Indori, Dohan and Kasavati and they all flow northwards from the south.
The climate of Haryana is similar to other states of India lying in the northern plains. It is very hot in summer (up to a high of 50 deg Celsius) and cold in winters (down to a low of 1 deg Celsius). The hottest months are May and June and the coldest being December and January. Rainfall is varied, with the Shivalik Hills region being the wettest and the Aravali Hills region being the driest. About 80% of the rainfall occurs in the monsoon season (July–September) and sometimes causes local flooding.



