Home ::India Map ::Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh is a state in Northern India. It is spread over 21,495 sq mi (55,673 km²), and is bordered by the Indian states of Jammu and Kashmir on the north, Punjab on the west and south-west, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh on the south, Uttarakhand on the south-east and by the Tibet Autonomous Region on the east. The literal meaning of Himachal Pradesh is Region of snowy mountains.
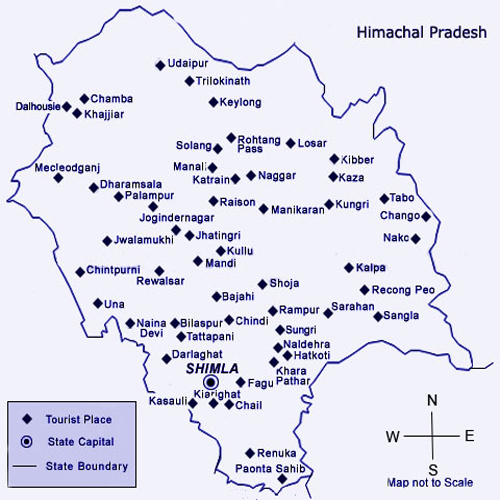
TOURIST ATTRACTIONS
Kullu
Kullu, once known as Kul-anti-peetha - "the end of the habitable world", is the capital town of the Kullu District, in the state of Himachal Pradesh, India. It is located on the banks of the Beas River in the Kullu Valley about ten kilometres north of the airport at Bhuntar. Kullu is a broad open valley formed by the Beas river between Manali and Largi. This valley is famous for the beauty and its majestic hills covered with Pine and Deodar Forest and sprawling Apple Orchards.The course of the Beas river presents a succession of magnificent, clad with forests of Deodar, yowering above trees of Pine on the lower rocky ridges. Kullu valley is sandwiched between the Pir Panjal, Lower Himalayan and Great Himalayan range.
Chamba, Himachal Pradesh
Chamba is an ancient town in the Chamba district in the state of Himachal Pradesh, in northern India. According to the 2001 Indian census, Chamba has a population of 38,312 people.Located at an altitude of 996 metres (3,268 ft) above mean sea level, the town is situated on the banks of the Ravi River (a major tributary of the Trans-Himalayan Indus River), at its confluence with the Sal River.
Though historical records date the history of the Chamba region to the Kolian tribes in the 2nd century BC, the area wasformally ruled by the Maru dynasty, starting with the Raju Maru from around 500 AD, ruling from the ancient capital of Bharmour, which is located 75 kilometres (47 mi) from the town of Chamba. In 920, Raja Sahil Varman (or Raja Sahil Verma) shifted the capital of the kingdom to Chamba, following the specific request of his daughter Champavati.From the time of Raju Maru, 67 Rajas of this dynasty have ruled over Chamba until it finally merged with the Indian Union in April 1948, although Chamba was under British suzerainty from 1846 to this time.
Kangra, Himachal Pradesh
Kangra is a city and a municipal council in Kangra district in the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. Historically known as Nagarkot, the town of Kangra was founded by Katoch Kshatriya Rajputs of Chandervanshi Lineage , who were rulers in Trigarta Central Asia. The Katoch Rajas had a stronghold here, with a fort and rich temples.Another ancient name of the city is Bhimagarand it was supposedly founded by Raja Bhim, younger brother of Kuru Emperor Yudhisthira of Indraprastha (now Delhi).
Khajjiar
Khajjiar is a hill station in Chamba district, Himachal Pradesh, India, located at an approximate of 24 km from Dalhousie .Khajjiar sits on a small plateau with a small stream-fed lake in the middle that has been covered over with weeds. The hill station is surrounded by green meadows and dense forests. It is about 6500 ft. (1981m) above sea level in the foothills of the Dhauladhar ranges of the Western Himalayas and snowy peaks can be seen in the distance.
Shimla
Shimla formerly known as Simla, is the capital city of Himachal Pradesh. In 1864, Shimla was declared the summer capital of the British Raj in India. A popular tourist destination, Shimla is often referred to as the "Queen of Hills," a term coined by the British. Located in the north-west Himalayas at an average altitude of 2,205 metres (7,234 ft), the city of Shimla, draped in forests of pine, rhododendron, and oak, experiences pleasant summers and cold, snowy winters. The city is famous for its buildings styled in tudorbethan and neo-gothic architecture dating from the colonial era. Shimla is connected to the city of Kalka by one of the longest narrow gauge railway routes still operating in India, the Kalka-Shimla Railway. Shimla is approximately 115 km (71.4 miles) from Chandigarh, the nearest major city, and 365 km (226.8 miles) from New Delhi, the national capital. The city is named after the goddess Shyamala Devi, an incarnation of the Hindu Goddess Kali.
Himachal Pradesh was anciently known as Dev Bhumi (The Abode of Gods). After the Anglo Gorkha War, the British colonial government came into power. It was initially part of Punjab, except the Siba State of Punjab Hills which was under the rule of Maharaja Ranjit Singh until 1857. In 1950 Himachal was declared as a union territory but after the State of Himachal Pradesh Act 1971, Himachal emerged as the 18th state of the Indian Union. Himachal has many prestigious boarding schools. Hima means snow in Sanskrit. It was named by one of the great Sanskrit scholars of Himachal Pradesh, Acharya Diwakar Datt Sharma
Himachal Pradesh has one of the highest per capita incomes of any state in India. Due to the abundance of perennial rivers, Himachal also sells hydro electricity to other states such as Delhi, Punjab and Rajasthan. The economy of the state is highly dependent on three sources: hydroelectric power, tourism and agriculture.
Hindus make up 95% of the state population, making it the most Hindu state (proportionally), in India. According to a 2005 Transparency International survey, Himachal Pradesh is ranked the second-least corrupt state in the country after Kerala.
Geography and climate
Himachal is situated in the western Himalayas. Covering an area of 55,673 kilometres (34,594 mi),Himachal Pradesh is a mountainous state with elevation ranging from about 350 metres (1,148 ft) to 6,000 metres (19,685 ft) above the sea level.
The drainage system of Himachal is composed both of rivers and glaciers. Himalayan rivers criss-cross the entire mountain chain. In fact the rivers are older than the mountain system. Himachal Pradesh provides water to both the Indus and Ganges basins. The drainage systems of the region are the Chandra Bhaga or the Chenab, the Ravi, the Beas, the Sutlej and the Yamuna. These rivers are perennial and are fed by snow and rainfall. They are protected by an extensive cover of natural vegetation.
There is great variation in the climatic conditions of Himachal due to extreme variation in elevation. The climate varies from hot and sub-humid tropical in the southern tracts to cold, alpine and glacial in the northern and eastern mountain ranges with more elevation. The state has areas like Dharamsala that receive very heavy rainfall, as well as those like Lahaul and Spiti that are cold and almost rainless. Broadly Himachal experience three seasons; hot weather season, cold weather season and rainy season. Summer lasts from mid April till the end of June and most parts become very hot (except in alpine zone which experience mild summer) with the average temperature ranging from 28 °C (82 °F) to 32 °C (90 °F). Winter lasts from late November till mid March. Snowfall is common in alpine tracts (generally above 2,200 metres (7,218 ft) i.e. in the Higher and Trans-Himalayan region).
Himachal was one of the few states that had remained largely untouched by external customs, largely due to its difficult terrain. With the technological advancements the state has changed very rapidly. It is a multireligional, multicultural as well as multilingual state like other Indian states. Some of the most commonly spoken languages includes Hindi, Punjabi, Pahari, Dogri, Mandialli Kangri, Gojri and Kinnauri. The Hindu caste communities residing in Himachal include the Brahmins, Rajputs, Gujjars, Gaddis, "Grith (choudhary)," Kannets (come under RAJPUTS), Rathis and Kolis.[34] There are also tribal population in the state which mainly comprise , Kinnars,Pangawals, Sulehria, and Lahaulis.
The state is well known for its handicrafts. The carpets, leather works, shawls, metalware, woodwork and paintings are worth appreciating. Pashmina shawl is one of the product which is highly in demand not only in Himachal but all over the country. Himachali caps are also famous art work of the people. Extreme cold winters of Himachal necessitated wool weaving. Nearly every household in Himachal owns a pit-loom. Wool is also considered as pure and is used as a ritual cloth. The well known woven object is the shawl, ranging from fine pashmina to the coarse desar. Kullu is famous for its shawls with striking patterns and vibrant colours. Kangra and Dharamshala are famous for Kangra miniature paintings.
Local music and dance reflects the cultural identity of the state. Through their dance and music, they entreat their gods during local festivals and other special occasions. Apart from the fairs and festivals that are celebrated all over India, there are number of other fairs and festivals also that are of great significance to Himachal Pradesh.
Shimla, the state capital is home to Asia's only natural ice skating rink.
The day to day food of Himachalis is very similar to the rest of the north India. They too have lentil, broth, rice, vegetables and bread. Some of the specialities of Himachal include Pateer, Chouck, Bhagjery, jhoul, Patrode, Sidku, Beduan, Chutney, Madra, Khatti Dal, Khatta and Ambua, Madra, Pahari Aloo and Pahari Murgh.



