Home :: West India :: Madhya Pradesh
WEST INDIA
MADHYA PRADESH
At the heart of India, the magic of Madhya Pradesh lies in its elegantly carved temples, proud fortresses and diversity of wildlife. Most of the state is a high upland, historically known as the Malwa region. Bhopal, the capital of Madhya Pradesh, is a charming amalgam of an old historic city, and modern urban planning.
The history of Madhya Pradesh goes back to the time of Ashoka, the grand Mauryan ruler. To the Chandelas, however, goes the credit of building the unbelievable monuments of Eros, Khajuraho, in the north of the state.
The state's cultural ancestry is ancient and checkered. Madhya Pradesh occupies a particular position in the history of music. The Gwalior gharana is among the most famous arbiters of style. The rivalry of Tansen and Baiju Bawra is remembered in incredible detail to this day.
Bhopal
The history of Bhopal dates back to the 11th century AD, when it was built by the renowned King Bhoja. The decline of the Mughal Empire with the death of Aurangzeb (AD 1707) led to following turmoil in this region. It was the second main Muslim state during the rise of British power in India. |
 Taj-Ul-Masjid |
Bhopal is the capital city of the state of Madhya Pradesh that is the biggest state in India. The city is also referred to as the City of Lakes for the reason that of the two gorgeous lakes that are situated in the center of the city.
Bharat Bhavan is a showcase of Indian art, folk traditions, monument and a centre for the performing arts too. Bhimbetka, a few hours' drive from Bhopal, is the site for impressive cave paintings; Udaygiri, another excursion from Bhopal, has prominent cave sculptures of religious themes.
Altitude - 572 meters,
Climate: (deg C)-Summer- Max 47.7, Min 24.9; Winter- Max 24.5, Min 9.1
Best Season - October to March.
Places Of Interest
Taj-ul-Masjid , Juma Masjid , Moti Masjid, Shaukat Mahal , Bharat Bhawan and Roopankar, Shamla and Idgah Hills. Chowk, Upper and Lower Lake , Gandhi Bhavan, Van Vihar.
Excursions
Bhimbetka- 40 kms, Bhojpur- 28 kms, Chiklod- 45 kms, Dhelwadi- 62 kms, Islamnagar-11 kms, Neori- 6 kms, Raisen- 47 kms, Sanchi- 46 kms, Vidisha- 56 kms, Ginnorgarh Fort- 61 kms.
Reach
By
Air: |
Well connected with all major towns. |
By Rail: |
Bhopal is well connected with all major cities. |
By Road: |
Bombay- 789 kms, Aurangabad- 588 kms, Ahmedabad- 571 kms, Agra- 523 kms, Delhi- 728 kms, Gwalior- 422 kms, Gwalior- 422 kms, Indore-187 kms, Ujjain- 189 kms, Sanchi- 46 kms, Khajuraho- 387 kms, Mandu- 290 kms, Pachmarhi- 210 kms. |
Sanchi
Sanchi is famous for its Stupas, monasteries, temples and pillars dating from the 3rd century BC to the 12th century AD. The Sanchi Stupa, the finest known of all, was initially built by the Mauryan Emperor Ashoka, then Governor of Ujjayini, whose wife Devi was the daughter of a merchant from the nearby Vidisha. Sanchi has the remarkable distinction of having specimens of almost all kinds of Buddhist architectural forms, stupas, chaityas, temples and monasteries - the finest examples of Buddhist imaginative art and sculpture in the country.
Altitude - 427 meters
Climate (deg C) - Summer- Max 45, Min 25; Winter- Max 22.5, Min 10
Best season - October to March.
Places Of Interest
Great Stupa No.1, Toranas or Gateways, Stupa No. 2, Stupa no. 3, Ashoka Pillar, Buddhist Vihara, Monasteries.
Excursions
Andhara and Pipalilya- 17.7 and 12 kms, Besnagar- 12 kms, Gyaraspur- 41 kms, Raisen Fort- 23 kms, Sonari and Satdhara-10 kms, Udaigiri- 13 kms.
Reach
By
Air: |
Nearest airport is Bhopal- 46 kms. |
By Rail: |
Nearest railhead is Bhopal 46kms. |
By Road: |
Bhopal- 46 kms, Vidisha- 10 kms, Indore- 232 kms etc. |
Gwalior
 Gwalior Temple |
According to a myth, Gwalior derives its name from a great sage Gwalipa who cured a ruler of the Kachwaha clan distress from leprosy. Gwalior's strategic place between north and south India made it a significant possession and was captured by several ruling houses. The first past holders of the city were the Huns. Held in series by the Mughals, Jats, Marathas and the British, Gwalior was lastly handed over to Jiyaji Rao Scindia at a official durbar in 1885. |
The Scindias were the previous ruling family of Gwalior and are still significant in the political arena of India. It is also holy to the memory of the daring queen Rani of Jhansi and Tatya Tope.
Area - 82 sq. km,
Altitude - 212 meters,
Climate (deg C) – summer 46 Deg. 21 Deg. Winter: 22 Deg. 6 Deg,
Best Season - October to March.
Places Of Interest
The Cenotraphs, Man Singh Palace, Man Mandir Palace, Gujari Mahal, Suraj Kund, Teli ka Mandir, Sas Bahu ka Mandir, Rani Jhansi Memorial, Tombs of Tansen and Ghaus Mohammad, Jai Vilas Palace, Gandhi Park, Zoo Municipal Corporation Museum, Jivaji Rao Scindia Museum.
Excursions
Tigra's Dam- 23 kms, Pawaya- 68 kms, Datia- 68 kms, Orchha- 120 kms, Shivpuri- 112 kms, Chanderi- 209 kms, Narwar- 128kms, Narwar Fort.
Reach
By
Air: |
Well linked all with major towns. |
By Rail: |
Gwalior is connected to all major cities in India. |
By Road: |
Agra- 118 kms, Bhopal- 420 kms, Delhi- 318 kms, Khajuraho- 280 kms, Sanchi- 344 kms, Shivpuri- 112 kms, Indore- 486 kms, Bombay-1086 kms. |
Orchha
 Mahal |
The medieval city of Orchha, in
the state of Madhya Pradesh, seems to have freezing in time,
its palaces and temples still retaining their unique grandeur.
Orchha had the sharing of being the capital of one of the
biggest and mainly powerful kingdoms of Central India. The
Bundela Rajput chieftain, Rudra Pratap, founded the city,
situated by the side of the gorgeous Betwa River, in the 16th
century. |
The word Orchha means 'hidden'. When the Tughlaqs, who were edict Delhi in the 15th century, pushed the Bundelkhand rajas out of Garkhundar, they retreated to distant Orchha.
Places Of Interest:
Jehangir Mahal, Raj Mahal, Raj Praveen Mahal, Ram Raja Temple, Chaturbhuj Temple, Laxmi Narayan Temple, Phool Bagh, Dinman Hardaul's Palace, Sunder Mahal, Cenotraphs, Shahid Smarak.
Reach
By
Air: |
Nearest airport is Gwalior -120 kms. |
By Rail: |
Nearest railhead is Jhansi -19 kms. |
By Road: |
Orchha lies on the Jhansi - Khajuraho road. |
Khajuraho
The fascinating temples of Khajuraho, India's exclusive
gift of love to the world, in the state of Madhya Pradesh, were
built among 950 and 1050 A.D. Khajuraho derives its name from the
Khajur tree (the date palm tree) which could be found in abundance
in the area. The heavenly sculptures in these temples are a compliment
to Life itself, embodying all that is sublime and impulsive about
it.
With the wane of the Chandela Empire, these superb temples lay neglected,
and susceptible to the ravages of Nature. It was only in this century,
that they were revived, restored and granted the gratitude that
they justly deserve.
OInitially there were 85 temples, of which only 22 still exist. These wonderful temples dedicated to Lord Shiva, Lord Vishnu and the Jain Tirthankaras. The three main compartments are the entry (ardhamandapa), meeting hall (mandapa), and the real sanctum (garbha griha). The temples are grouped into three ecological divisions: western, eastern and southern.
Climate (deg C) -Summer 47 Deg. C. 21 Deg. C, Winter 32 Deg. C. 4 Deg. C,
Rainfall - 114 cm. (July-September),
Best Season - October to March.
Excursions
Dhubela Museum- 64 kms, Beni Sagar- 11 kms, Panna Diamond Mines- 56 kms, Panna National Park- 60 kms, Pandav Falls- 35 kms, Raigarh Palace- 25 kms, Raneh Falls- 20 kms, Ranguan Lake- 25 kms, Ajaygarh Fort- 80 kms, Kalingar Fort- 125 kms, Nachana- 100 kms.
Places Of Interest
The temples of Khajuraho are divided into three geographical groups viz, Western, Eastern, and Southern groups.
Western Group of Temples:
Chausath Yogini Temple, Kandariya Mahadeo Temple, Devi Jagdamba Temple, Chitragupta Temple,Vishwanath Temple, Parvati Temple, Lakshmana Temple, Matangeshwara Temple.
Eastern Group of Temples:
Brahma Temple, Vamana Temple, Parsvanath Temple, Ghantai Temple.
Southern Group of Temples:
Dulhadeo Temple, Chaturbhuj Temple, Archaeological Museum.
Reach
By
Air: |
Well connected with Delhi. |
By Rail: |
Jhansi-175 kms, Satna-117 kms, Harpalpur-110 kms. |
By Road: |
Agra- 395 kms, Allahabad- 285 kms, Bandhavgarh- 237 kms, Bhopal- 372 kms Chitrakoot- 176 kms, Delhi- 590 kms, Jabalpur- 296 kms Lucknow- 267 kms, Varanasi- 415 kms. |
Indore
Planned and built by Rani Ahilyabai,
the valiant Holkar queen, Indore lies to the great west of
Madhya Pradesh on the banks of the rivers Saraswati and Khan
which join at the centre of the city. Indore derives its name
from the 18th century Indreshwar Temple. |
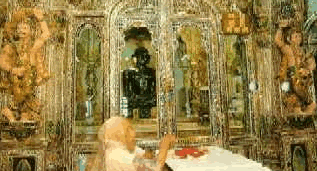 Indreshwar Temple |
The history of Indore is indissoluble from the history of the Holkar State. The founder of the House of Holkars was Malhar Rao Holkar, born in 1693 AD. Ahilya Bai was one of the leading Maratha personalities and an astonishing woman ruler of India. She was the rare Indian royals who were deified in her lifetime.
Though Ahilya Bai esteemed Indore immensely, it was only after her death that the State capital was shifted from Maheshwar to Indore in 1811 AD. Today, her statue decorates the centre of the city, Rajwada.
Climate (deg C) - Summer Max- 40.5, Min- 27; Winter Max- 30.4, Min- 15,
Rainfall - 110 cms (July to September),
Best Season - September to March.
Places Of Interest
Chhatri Bagh, Gita Bhavan, Lalbaug Palace, Bada Ganapati, Juna Rajwada, Kanchi Mandir or Hukumchands Temple, Annapurna Temple, Kendriya Sangrahalaya.
Excursions
Bagh Caves-153 kms, Ujjain- 53 kms, Mandu- 99 kms, Maheshwar- 90 kms, Omkareshwar- 77 kms.
Reach
By
Air: |
Indore is well linked all major cities. |
By Rail: |
Indore is well connected to major cities of India. |
By Road: |
Agra- 605 kms, Ahmedabad- 456 kms, Bhopal- 187 kms, Bombay- 602 kms, Delhi- 809 kms, Gwalior- 486 kms, Khajuraho- 574 kms, Maheshwar- 90 kms, Mandu-105 kms, Ujjain- 53 kms. |
Ujjain
Ujjain, one of the sites of the Kumbh Mela. This mela celebrates the saving of the earth by Lord Shiva and the churning of the ocean by the Gods and The Demons to retrieve the Kumbh (The pot of Amrit, the nectar of immortality). Emperor Ashoka spent his years of tutelage as the viceroy of Pataliputra here in Ujjain. Under the Guptas and the Paramara kings, Ujjain was a centre of trade and scholarship. The Vikramaditya University founded by the erudite King Vikramaditya also used Ujjain as its base. One of the oldest and holiest of Indian cities, Ujjain is located on the banks of river Shipra.
Altitude - 492 meters,
Climate (deg C) - Summer- Max. 40, Min. 20; Winter- Max. 28, Min. 10,
Rainfall - 101 cms (July to September),
Best Season - September to March.
Places Of Interest
Bharatahari Cave, Gopal Mandir, Jantar Mantar, Kailadah Palace, Mahakali Temple, Sandipani Ashram, Shipra Ghats, Vikram University Museum.
Excursions
Agar- 66 kms, Devas- 37 kms, Maksi- 39 kms, Nagada- 60 kms.
Reach
By
Air: |
Nearest Airport is Indore-53 kms. |
By Rail: |
Ujjain is well connected to all major towns. |
By Road: |
Ahmedabad- 402 kms, Bhopal-183 kms, Bombay- 655 kms, Delhi- 774 kms, Gwalior- 451 kms, Indore- 53 kms and Khajuraho- 570 kms. |
Kanha National Park
Kanha National Park in the Mandla District spreads over 1,945 sq.km of dense sal forests, scattered with extensive meadows and trees and clumps of wild bamboo Situated in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh, the charming Kanha National Park was the inspiration behind Rudyard Kipling's unforgettable classic Jungle Book. By far the most outstanding features of this area are the open grassy meadows, where sighting blackbuck, slough deer, sambhar and chital is common. And, if one could transcend into time, a barefooted Mowgli will perhaps come padding along the dusty trail, for this is the land of Kipling's Jungle Book. |
 Kanha National Park |
If one were to point to the center of India, chances are he would pick out the forests of the Banjar and the Halon valley, the two forming the western and eastern halves of the Kanha Tiger Reserve, which have long been well-known for their wide diversity of wildlife.
Area - 1,945 sq.kms,
Altitude - 600-900 meters.
Climate (deg C) - Summer- Max 40.6, Min 23.9; Winter- Max 23.9, Min 1.1.
Rainfall - 152 cms,
Best Season - April to June and November to January. (The park is closed from July to Mid November during monsoon)
Wildlife in the park:
The main attractions are Tiger, Bison, Gaur, Sambar, Chital, Barasingha, Barking Deer, Black Deer, Black Buck, Chousihgha, Nilgai, Mouse Deer, Sloth Bear, Jackal Fox, Porcupine, Hyaena, Jungle Cat, Python, Pea fowl, Hare, Monkey, Mongoose, Tiger, Leapord etc. can also be seen here.
Birds species in the park:
Storks, Teals, Pintails, Pond Herons, Egrets, Peacock, Pea Fowl, Jungle Fowl, Spur Fowl, Partridges, Quails, Ring Doves, Spotted Parakeets, Green Pigeons, Rock Pigeons, Cuckoos, Papihas, Rollers, Bee Eater, Hoopoes, Drongos, Warblers, King Fishers, Wood Peckers, Finches, Orioles, Owls, Fly Catchers.
Reach
By
Air: |
Nagpur- 266 kms is the nearest airport. |
By Rail: |
Jabalpur-169 kms is the nearest rail. |
By Road: |
Jabalpur- 175 kms, Khajuraho- 445 kms, Nagpur- 266 kms, Mukki -25 kms, Raipur- 219 kms. |
Bandhavgarh National Park
Set amongst the Vindhyas, in Madhya Pradesh, Bandhavgarh
is a tiny national park, but with the peak known density of tiger
population in India. This is also known as White Tiger territory.
These have been found in the old state of Rewa for many years. Besides
its charming scenery formed by the Sal forest in the valleys and
regal tree clad hills in the back-drop.
The Park is spread over an area of 437 sq. km. The terrain is made
of rocky hills, sal forests and grazing areas, previously agricultural
land. The finest of these hills is the Bandhavgarh hill, and on
its peak point stands Bandhavgarh Fort.
Several dynasties have ruled the fort: for instance, the Maghas from the 1st century A.D, the Vakatakas from the 3rd century; the Sengars from the 5th century, and the Kalachuris from the 10th century. The oldest signs of habitation are the cave dug into the sandstone, near the fort. Several of these have Brahmi inscriptions dating from the 1st century B.C.
Area - 280 sq. kms,
Altitude - 400 to 810 meters,
Climate (deg C) - Summer- Max 41.4, Min 26; Winter- Max 21.1, Min 9.6,
Rainfall - 1174 mms,
Best Season - March to June. The park is closed from July to Mid-November.
Wildlife in the park
Tiger, Leopard, Bear, Bison, Chital, Sambhar, Nilgai,Chinkara, Chowsingha,Barking deer, Wild Pig, Hyaena, Porcupine.
Birds species in the park
Peacock, Paradise fly catchers, Jungle Fowl, Golden and Black headed Orioles, Yellow Ioras, Red-vented Bulbuls, Blue Jays, Purple Sunbirds, Green Barbets and Mynahs.
Reach
By
Air: |
Khajurao- 230 kms is the most nearest airport. |
By Rail: |
The nearest railhead Umaria- 30 kms and Satna- 117 kms. |
By Road: |
Khajuraho- 230 kms, Varanasi- 340 kms, Katni- 75 kms, Rewa- 115 kms, Umaria- 30 kms, Kanha- 250 kms. |
STATES OF WEST INDIA
- Daman & Diu
- Gujarat
- Goa
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra



